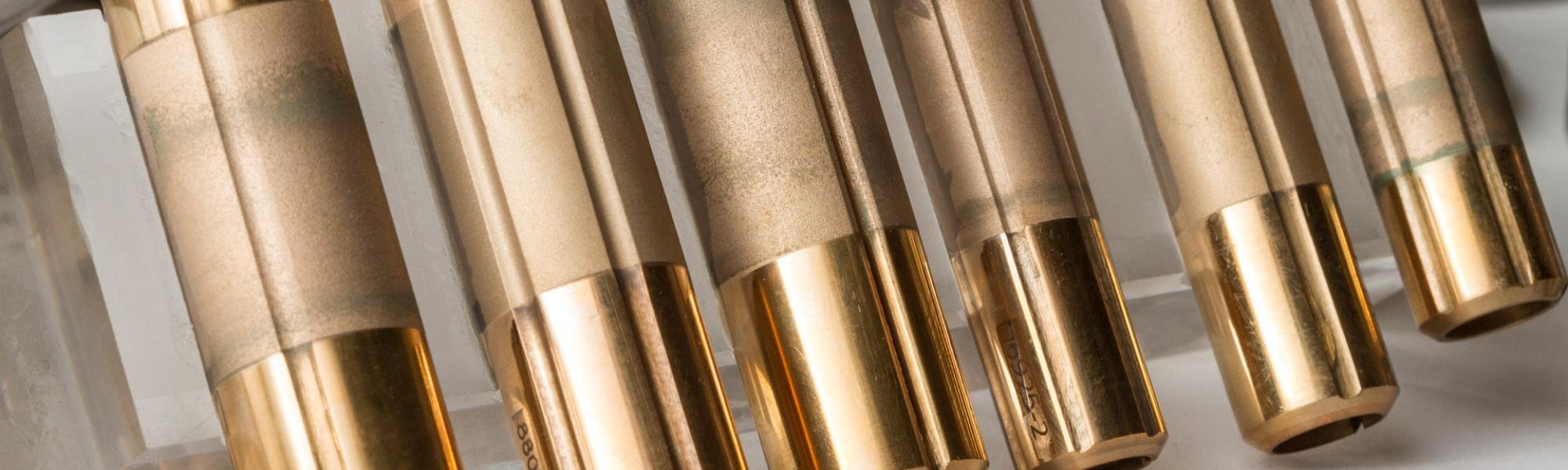
HIGH PERFORMANCES THANKS TO THE USE OF TOP QUALITY NOT COATED POWDERS
METALLIC WHEELS
Metallic bond wheels are used in grinding operations on abrasives, hard metals, glass, ceramics and graphite. These wheels are realized at temperatures of 500-800°C: their structure is in metal and not in resin, so they reflect light more than the resinoid ones.

TYPES OF SUPER ABRASIVE TO USE
The following table indicates the super abrasive to use in base of wheel material.
| WITH DIAMOND | WITH CUBIC BORON NITRIDE (CBN) |
|---|---|
|
Hard Metals - Cermet - Fiberglasses - Graphites - Refractory Materials - Glass - Ferrite - Oxyceramic Materials - Porcelain - Friction Materials - Carbonglass Composites - Kevlar |
High Speed Steels |
CONCENTRATION
The choice of the concentration depends on a series of factors like sharpening speed, use or not of refrigerants, profile sealing, worked material and grain.
High concentration does not always ensure high performance of the wheel.
| NAME | SYMBOL | ct./cm³ |
|---|---|---|
| BASSA - BASSE - LOW MEDIA - DEMIE - MEDIUM FORTE - FORTE - STRONG EXTRA - EXTRA - EXTRA |
C50 C75 C100 C150 |
2,2 3,3 4,4 6,6 |
WHEEL ASSEMBLY
Wheel assembly on the mandril is very important for the effects of finishing quality and performance. It is necessary to control with the help of a comparator that concentricity and flatness errors on the rotation axis are not over 0,02 mm.
DRESSING
If there is a wheel sharpening loss, it is necessary to dress it through a bar of common abrasive, making a light pressure in way to not damage CBN or diamond crystals.
GRANULOMETRY
Granulometries used in CBN and diamond wheels construction are categorized according to FEPA rules, that are reported compairing to the other rused more commonly used.
GRAIN AND ROUGHNESS
The following table shows roughness values with the use of various grains. These instructions are approximate, because the effective roughness is influenced by grain, working features, machine stiffness, characteristics of refrigerant liquid and entity of contact sufaces.
| FEPA GRAIN | Ra (μm) | CLA (μ”) |
|---|---|---|
| 181 | 1,8 - 3,2 | 63 - 126 |
| 107 | 0,8 - 1,6 | 32 - 63 |
| 76 | 0,4 - 0,8 | 16 - 32 |
| 54 | 0,2 - 0,4 | 8 - 16 |
| 15 | 0,1 - 0,2 | 4 - 8 |
| 7 | 0,005 - 0,1 | 2 - 4 |
CUT DEPTH
This parameter is related to diamond granulometry and influences the superficial finishing state of the workpiece. In roughing works with medium-high granulometries, it is possible to cut from 0,03 to 0,06 mm and also higher.
In finishing, with fine grains, it shouldn't overcome 0,006 mm per cut: cut depth influences also the wheel wear.
PERIPHERAL SPEED
Peripheral speed represents the relative speed of slipping between the diamond band and the area of the workpiece. This speed is usually given by the peripheral speed of diamond wheel, because the piece is stationary or has a negligible movement respect to the wheel.
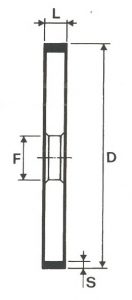
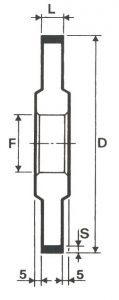
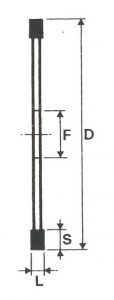
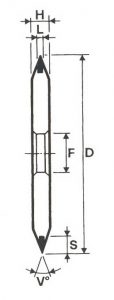
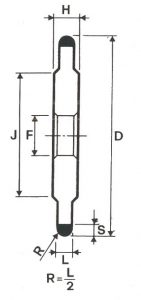
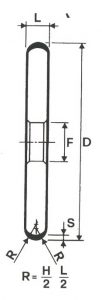
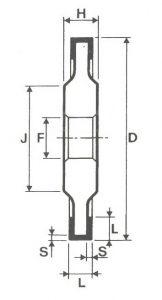
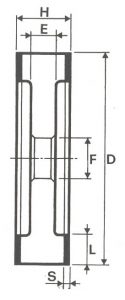
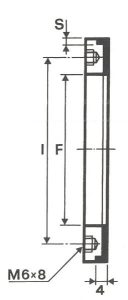
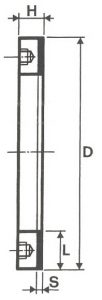
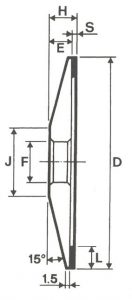
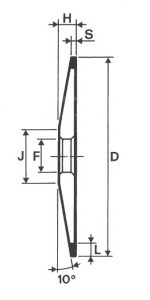
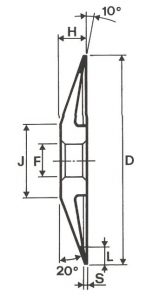
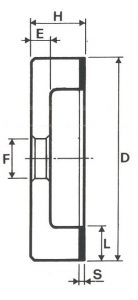
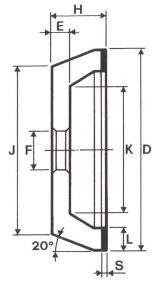
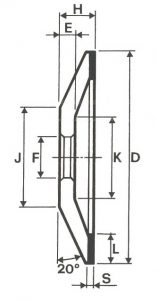
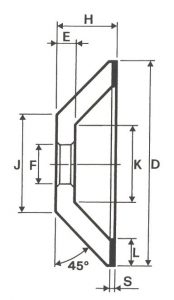
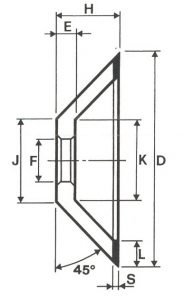
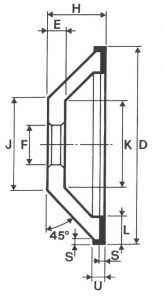
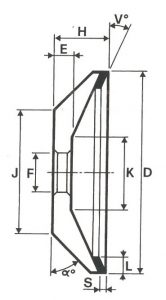
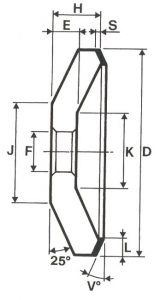
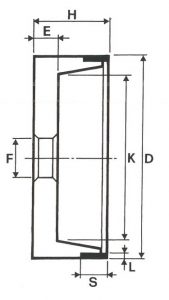
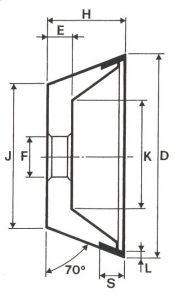
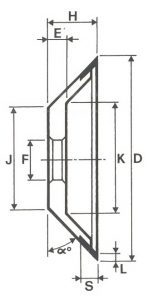
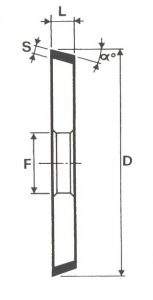
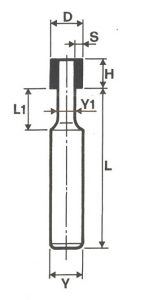
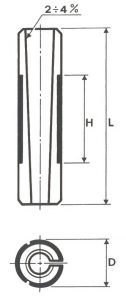
SHAPES
LITD produce every type of wheel, with diameters from 20 mm to 500 mm of different thickness and band shapes. Customers can have special facilities on request, with minimum quantity of production.
REFRIGERANT
In grinding processing with diamond and CBN wheels, where it is possible, it is recommended to use a refrigerant liquid: this avoid clogging phenomena of abrasive band with thermal decay of the wheel.